How Inflammation Impacts Weight Gain And Your Health
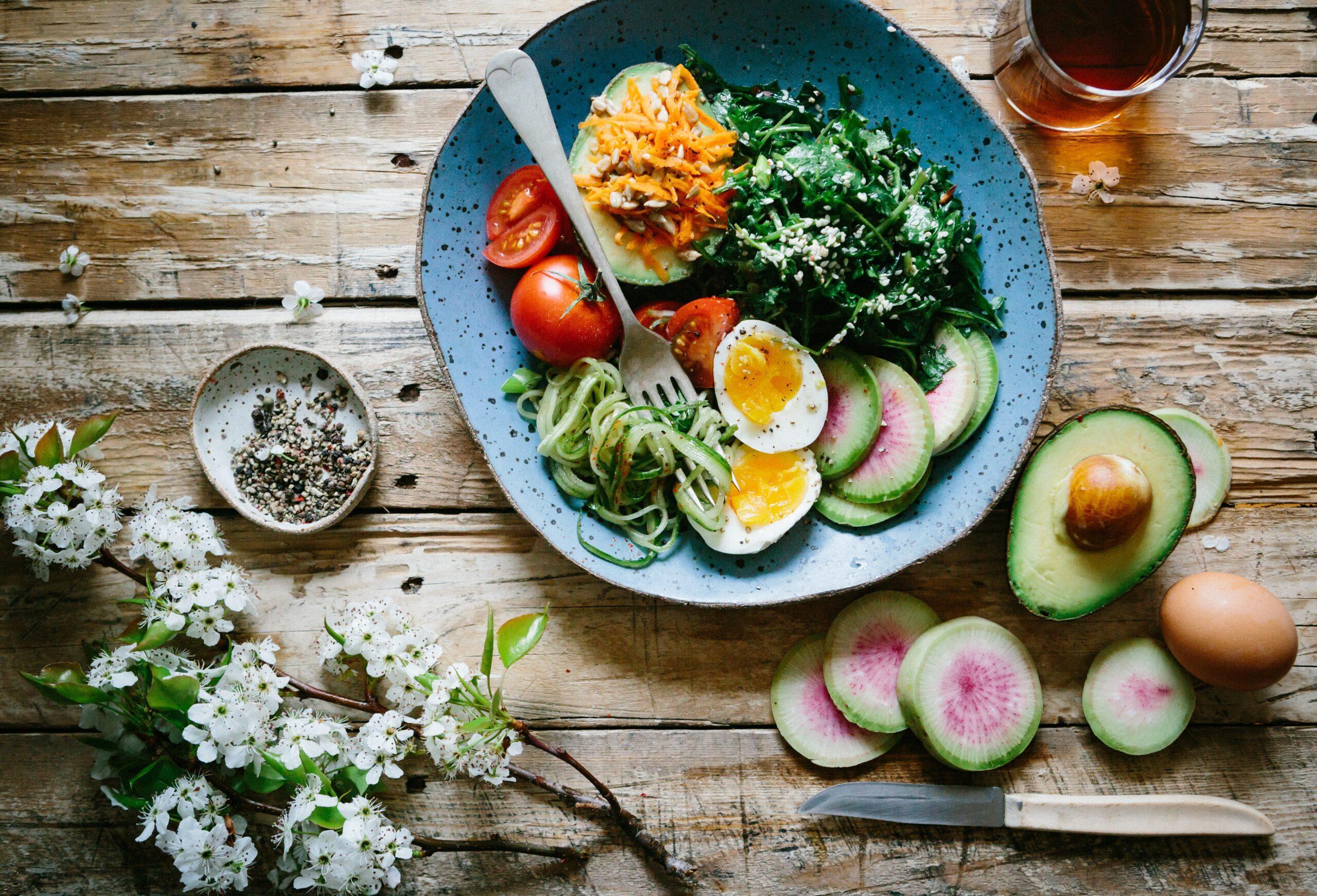

There are so many factors that can affect our ability to lose weight and keep it off, and one of the biggest ones is chronic inflammation.
Inflammation touches nearly every aspect of overall wellness, including how hard it is to stay at a healthy weight. Food intolerances, stress, underlying health conditions, and microbiome imbalances are all triggers for inflammation and, as a result, issues with weight loss.
They may seem complicated at first, but once you understand the connections between inflammation, weight, and health, you can find ways to overcome these challenges and achieve positive outcomes for you and your overall well-being.
Inflammation And Weight Gain
Inflammation and weight gain have a complex relationship. One can cause the other, resulting in a vicious cycle. Habits like overeating, for example, can trigger the immune system and cause the body to generate proinflammatory cytokines, but chronic inflammation can affect the inverse, too.
Chronic inflammation disrupts hormonal signals that regulate appetite and fat storage. It can lead to insulin resistance and leptin resistance. (1) Both impair your brain’s ability to recognize satiety and when the body has enough fat stored, this can drive overeating.
Elevated levels of cortisol, a stress hormone that rises with inflammation, promote the accumulation of belly fat. (2) If you’re constantly stressed, that only leads to more inflammation, creating a cycle of fat gain and extended inflammatory responses.
Chronic inflammation also affects mitochondrial function. (3) This can reduce energy production, slow your metabolism, and impact calorie-burning. If you’re feeling tired all the time, inflammation is often the culprit.
Both chronic and acute inflammation also disrupt the gut microbiome, an essential community of bacteria involved in metabolism and appetite regulation. (4) Inflammatory diets high in processed foods can alter your microbiome’s composition and mess with your body’s hunger signals (not to mention hormonal health, mental health, and overall functioning).
Clearly, the calories in/calories out idea we were all taught as kids isn’t going to cut it anymore. Inflammation touches every aspect of wellness, including weight, and it’s important to do our best to reduce inflammation for effective weight loss and better health.
How Chronic Diseases Are Involved
Chronic diseases can make weight management and inflammation control even tougher. They’re not just triggers for inflammation, which you now know is linked to weight loss resistance. These health issues can affect appetite, fat storage, and insulin resistance.
It’s also important to note that both obesity and inflammation are risk factors for many conditions out there that, in turn, make it more challenging to lose weight. It’s a cycle that requires meaningful management to reduce health risks and get you back on track for optimal health.
Diabetes
Diabetes and weight gain are closely linked through insulin resistance and chronic inflammation. (5) In Type 2 diabetes, your cells become resistant to insulin, causing the pancreas to produce more of it. High insulin levels promote fat storage, especially in the belly, leading to weight gain.
Chronic inflammation can worsen insulin resistance, leading to more weight gain, elevated blood sugar levels, and even more inflammation. As you gain weight, your metabolism is disrupted even further.
Managing diabetes involves reducing inflammation through diet, exercise, and medication as needed to improve insulin sensitivity.
Arthritis
Arthritis means "inflammation of the joints". Both rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are characterized by inflammation in the joints and often come alongside systemic inflammation throughout the body. The pain and stiffness patients feel with this condition can make physical activity difficult, which can also lead to weight gain.
Excess weight further strains the joints, (6) exacerbating arthritis symptoms and creating this feedback loop of pain and inflammation. Managing the condition often involves anti-inflammatory diets, gentle exercise, and therapies to return some mobility to the joints.
You can reverse autoimmune symptoms from conditions like arthritis and reduce inflammation naturally. Learn more in my course, Mastering Autoimmune Conditions & Inflammation With Functional Medicine.
Cardiovascular Disease
Heart disease often involves chronic inflammation, which can lead to more fat storage, especially around the belly. That excess fat, already a risk factor for heart disease alongside cholesterol and high blood pressure, increases inflammation and puts stress on the heart and blood vessels. (7)
As an added bonus, common medications like beta blockers that aim to improve heart health and lower your blood pressure may increase body weight due to their effects on your metabolism. (8)
Physical activity, so important for heart health, can be hard to maintain with heart conditions or excess weight, making it even more challenging to manage weight. Anti-inflammatory diets, gentle exercise, and stress management are essential for managing weight with a heart condition.
Gut Conditions
Gut inflammation and weight gain disrupt the balance of bacteria in the microbiome. This can lead to increased gut permeability (leaky gut) and trigger further inflammation. Excess body fat can also lead to the release of inflammatory molecules that impair digestion, leading to bloating and discomfort.
This can increase your risk of gut conditions like acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease. All of these conditions can be worsened by both inflammation and obesity.
On the other hand, an imbalanced gut microbiome can drive weight gain by increasing inflammation, slowing your metabolism, and affecting hunger hormones. (9) This creates a cycle where poor gut health and weight gain reinforce each other.
Recognizing Inflammation
In addition to weight gain and weight loss resistance, inflammation can manifest in symptoms that affect all areas of your body. Signs that you’re dealing with inflammation can include:
- Moodiness
- Persistent fatigue
- Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
- Depression and/or anxiety
- Gut problems (e.g. bloating, constipation, gas, IBS flare-ups)
- Skin problems (e.g. acne, eczema, rashes)
- Frequent infections of illnesses
- Headaches
- Water retention
- Muscle aches and/or joint pain
- Blood sugar imbalances
For an in-depth overview of inflammation and tools to reduce inflammation in your body for better health, check out my book, The Inflammation Spectrum.
How To Start Healing
There is no one-size-fits-all solution for lowering inflammation, but there are many natural tools that help to reduce chronic inflammation and its impact on your weight.
Reassess Your Diet
There’s no one way to approach dietary changes when it comes to inflammation, but you can start by cutting inflammatory foods like sugar, dairy, and gluten-containing grains out of your eating plan. From there, even foods that are generally considered healthy could contribute to low-grade inflammation.
I recommend doing an elimination diet in order to discover which foods are irritants and aren’t working for you. By uncovering hidden food intolerances and sensitivities, you’ll be well on your way to winning the battle against inflammation.
On the flip side, you should also incorporate anti-inflammatory foods into your diet. Here’s a short list:
- Leafy greens
- Avocados
- Ginger
- Turmeric
- Berries
- Nuts
- Olive oil
- Green tea
- Fatty fish*
*Fatty fish like salmon, herring, and mackerel are a favorite among healthcare providers for a reason. They’re a good source of healthy fats and omega-3 fatty acids known to boost immune response and fight against high levels of inflammation.
Proactively Work On Healing Your Gut
Our gut microbiome plays a huge role in weight management, and inflammation can create an additional obstacle to a balance of good vs. bad bacteria in your gut. (10) Imbalances in your microbiome influence your metabolism, appetite, and fat storage (to name a few).
What you eat matters. Certain problematic bacteria thrive on processed foods and sugars, creating a space more welcoming to inflammation and, as a result, gut dysregulation. A disrupted microbiome also reduces energy efficiency, meaning you’re burning fewer calories.
Healing the gut starts with diet. The anti-inflammatory foods I’ve already listed are a great start. Add probiotics found in foods like yogurt, kefir, or kimchi, or take a good quality supplement.
Incorporate prebiotics found in foods including garlic, artichokes, and asparagus to feed beneficial gut bacteria. Eat fiber-rich foods to encourage bacterial diversity, which is linked to better weight regulation.
Note that there are always exceptions here. For example, those with histamine intolerance may have an inflammatory response to probiotic foods, as fermented foods are high in histamine. And those with SIBO may react to certain prebiotic foods that are high in FODMAPs. This is why both an elimination diet and, often, specialized testing with a functional medicine practitioner, are so helpful in order to customize the best eating plan for YOUR gut.
And on the same note, make sure to always listen to your body. The gut-brain connection is powerful, and barriers to that connection, like chronic stress, can affect the microbiome and undermine your weight loss efforts.
Get Adequate Sleep
Many studies have found that getting adequate sleep each night is essential for healthy inflammation levels, especially in women. (11) Just one night of poor sleep can cause inflammation levels to increase, and quality sleep is just as important as the number of hours you sleep.
Work on cultivating a bedtime routine that works for you. That may mean no electronics before bed, weighted blankets, and/or stress relief tools like aromatherapy so that you can get at least 7 hours of uninterrupted shut-eye.
Try Detoxing
Everyone can benefit from a detox. We’re exposed to toxins on a daily basis that contribute to inflammation, fatigue, gut issues, problems with our skin, and difficulties losing weight. It’s not enough to start every morning with a green smoothie, though.
It's important to limit toxin exposure and support detoxification at the same time. That can look like switching out products around the house to non-toxic versions and introducing foods that support methylation pathways and liver function.
Antioxidant-rich leafy greens and vitamin B-rich superfoods like organ meats and other grass-fed lean proteins are a great start. You can learn more about detoxing in my guide here.
Exercise Consistently
Regular exercise isn’t just good for burning calories. It supports sustainable weight loss by boosting your metabolism, improving immune function, and balancing your hormones. Movement is good for your microbiome and strengthens your gut barrier, helping to prevent leaky gut. (12)
Exercise also helps regulate insulin and blood glucose to prevent excess fat storage, reducing your risk of negative diabetes outcomes and chronic inflammation linked to obesity.
Take Care Of Your Mental Health
Your mental well-being directly impacts your physical health. Strengthening that mind-body connection can be a powerful tool in your efforts to lower inflammation and achieve a healthier weight.
High cortisol levels can trigger inflammation and encourage fat storage. By alleviating chronic stress, you support balanced cortisol levels and other hormones that impact inflammation. Stress also disrupts appetite-regulating hormones, causing cravings that can lead to weight gain.
Lowering stress through techniques like mindfulness, exercise, or deep breathing helps to calm your mind, decrease cortisol, and reduce inflammation. Make it a daily routine.
If you need support, tap into your network of family and friends. Community is essential when it comes to stress management, especially if you’re dealing with long-term struggles with your weight.
Inflammation And Weight Can Be Managed
By making healthy lifestyle choices, you can decrease inflammation and lose excess weight to reverse the cycle of inflammation to weight gain and back again. If you’re not sure where to start, an elimination diet and incorporating foods with anti-inflammatory effects into your diet is a great step.
If you think you're struggling with inflammation, or you're wondering what's behind your weight loss resistance, a functional medicine provider can support you with an individualized approach to your health. At our telehealth clinic, we start with a comprehensive review of your health history and will often run specialized labs including (but beyond) C-reactive protein (CRP) tests, which look for inflammatory markers to pinpoint your unique health concerns.
From there, we can develop a treatment plan tailored to your health needs to help you break the cycle for good.
As one of the first functional medicine telehealth clinics in the world, we provide webcam health consultations for people around the globe.
View More At Our Store
Purchase personally curated supplements
and Dr. Will Cole’s books!

- Li, H., Meng, Y., He, S., et al. (2022). Macrophages, chronic inflammation, and insulin resistance. Cells, 11(19), 3001.
- Johar, H., Spieler, D., Bidlingmaier, M., et al. (2021). Chronic inflammation mediates the association between cortisol and hyperglycemia: findings from the cross-sectional population-based KORA age study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(13), 2751.
- Nesci, S., Spagnoletta, A., & Oppedisano, F. (2023). Inflammation, mitochondria and natural compounds together in the circle of trust. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6106.
- Al Bander, Z., Nitert, M.D., Mousa, A., et al. (2020). The gut microbiota and inflammation: an overview. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(20), 7618.
- Tsalamandris, S., Antonopoulos, A.S., Oikonomou, E., et al. (2019). The role of inflammation in diabetes: current concepts and future perspectives. European Society of Cardiology, 14(1), 50-59.
- Vincent, H.K., Heywood, K., Connelly, J., et al. (2012). Obesity and weight loss in the treatment and prevention of osteoarthritis. PM&R Journal, 4(5 Suppl), S59-67.
- Khafagy, R. & Dash, S. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: the emerging role of inflammation. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 8, 768119.
- Messerli, F.H., Bell, D.S., Fonseca, V., et al. (2007). Body weight changes with beta-blocker use: results from GEMINI. The American Journal of Medicine, 120(7), 610-615.
- Davis, C.D. (2016). The gut microbiome and its role in obesity. Nutrition Today, 51(4), 167-174.
- Noor, J., Chaudhry, A., Batool, S., et al. (2023). Exploring the impact of the gut microbiome on obesity and weight loss: a review article. Cureus, 15(6), e40948.
- Dzierzewski, J.M., Donovan, E.K., Kay, D.B., et al. (2020). Sleep inconsistency and markers of inflammation. Frontiers in Neurology, 11, 1042.
- Mailing, L.J., Allen, J.M., Buford, T.W., et al. (2019). Exercise and the gut microbiome: a review of the evidence, potential mechanisms, and implications for human health. Exercise and Sports Sciences Reviews, 47(2), 75-85.
The information on this website has not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration or any other medical body. We do not aim to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any illness or disease. Information is shared for educational purposes only. You must consult your doctor before acting on any content on this website, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition.
Our content may include products that have been independently chosen and recommended by Dr. Will Cole and our editors. If you purchase something mentioned in this article, we may earn a small commission.

BY DR. WILL COLE
Dr. Will Cole, DNM, IFMCP, DC is a leading functional medicine expert who consults people around the globe, starting one of the first functional medicine telehealth centers in the world. Named one of the top 50 functional and integrative doctors in the nation, Dr. Will Cole provides a functional medicine approach for thyroid issues, autoimmune conditions, hormonal imbalances, digestive disorders, and brain problems. He is also the host of the popular The Art of Being Well podcast and the New York Times bestselling author of Intuitive Fasting, Ketotarian, Gut Feelings, and The Inflammation Spectrum.

Gut Feelings
Healing The Shame-Fueled Relationship
Between What You Eat And How You Feel