How To Reverse Leptin Resistance (Plus Symptoms and Causes You Need to Know)

Leptin resistance is one of the most overlooked hormonal imbalances, and it could be why weight loss feels like an uphill battle no matter how clean you eat or how much you exercise.
It's one of the most common hidden drivers of weight gain that I see in my telehealth practice, and it's nearly impossible to turn this condition around on your own if you don't know what's going on.
A functional medicine approach can help you get to the root of your weight loss resistance for more sustainable treatment and long-term weight management. Let's get into it.
A Closer Look At Leptin Resistance
Leptin is a hormone produced in the adipose tissue by adipocytes, or fat cells, that regulate hunger and energy balance. (1)
One of leptin’s jobs is to tell your brain to use the body’s fat stores for energy. Leptin resistance occurs when the hypothalamic cells in the brain stop responding to or recognizing leptin’s signals. (2)
When this happens, your brain will turn on all of the hunger signals it can to make up for what it thinks is a food deficit and help your body get back to energy homeostasis. You could simply look at food and gain weight if you’re experiencing issues with your leptin system.
Leptin also influences the activity of neuropeptides (chemical messengers that regulate hunger and satiety). Impaired leptin signaling can cause these messengers to go into overdrive, increasing cravings and appetite.
A big trigger for leptin resistance is chronic inflammation, which dulls the brain’s leptin receptor sites. Impaired signaling pathways cause your body to produce more leptin to account for what it believes are low leptin levels, resulting in hyperleptinemia, or high levels of leptin. (3)
Those already struggling with obesity and/or high triglycerides are at a higher risk of leptin resistance because of the effects of both on the blood-brain barrier.
Patients with uncontrolled diabetes and imbalanced insulin levels may also have issues with leptin sensitivity. (4) Addressing leptin resistance can improve insulin sensitivity and vice versa.
Sleep deprivation, stress, a high-fat diet, and a lack of exercise can make your symptoms worse and increase leptin concentrations.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of leptin resistance include:
- Difficulty losing weight and keeping it off
- Overeating
- Constant hunger or hyperphagia (abnormally high appetite)
- Food cravings, especially for sugar
- Excess body mass, particularly in your mid-section
- High blood pressure (5)
- High cholesterol
- Chronic fatigue
- Body pain (6)
- Sleep issues
- Difficulties managing stress
- Insulin resistance
Long-term leptin resistance can lead to more weight gain and a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, fatty liver disease, and metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes. (7)
Low leptin levels, or hypoleptinemia, are less common and generally caused by congenital leptin deficiency or mutations in the leptin gene. They may also happen as a result of eating disorders. (8)
Low leptin symptoms include fatigue, trouble concentrating, mood swings, and a reduced metabolism.
Healing From Leptin Resistance
As with most health journeys, treating leptin resistance starts with the basics of reducing stress, getting good sleep, and eating the right foods. When it comes to leptin resistance, medications will never get to the root of the problem, like optimizing these fundamental parts of your lifestyle.
A holistic, functional medicine approach is also not just focused on helping you lose weight, but helping you restore your overall health and wellbeing.
Run The Right Tests
To determine if a patient truly has leptin resistance and not some other underlying condition, I run a simple blood test to measure serum leptin levels. Optimal fasting leptin levels should be 4 to 6 ng/dL.
This lab isn’t commonly run in mainstream medicine because there is no medication for it. If there were, everyone would be tested for high leptin.
If labs confirm leptin resistance, I’m not necessarily done with testing. In functional medicine, we always want to get to the root cause so that we can actually reverse the problem from the source. So if your hormone receptors aren’t responding to leptin, I will often run additional tests to try to figure out why.
Depending on your other symptoms, risk factors, and individual health profile, these may include additional hormone tests, gut microbiome testing, and/or testing for inflammatory markers.
Cultivate A Healthy Sleep Routine
People with poor sleep habits are more likely to be leptin-resistant. Inadequate sleep can also disrupt the balance of ghrelin, another hunger hormone, messing with your satiety even further. (9) Aim for a consistent sleep schedule of 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
If you’re having trouble getting to bed, prioritize your nightly routine. Avoid caffeine close to bedtime and find what works to calm your brain, like reading or meditating. Put down the smartphone at least an hour or 2 before going to sleep.
Avoid the late-night snacks. Eating after 8 p.m. is associated with higher leptin resistance levels and more weight gain.
Implement Specific Dietary Changes
There is no single diet to get your leptin levels in the ideal range. Since leptin is a peptide hormone, not a nutrient, there are no foods high in leptin, either. But if you’re looking to reverse leptin resistance, you can absolutely use food to help target the causes.
Eat a diet high in fiber over carbohydrates to support satiety and stabilize your blood sugar. High-fiber foods include a variety of vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
It's also worth incorporating foods that support secretion of another hormone, GLP-1 (which promotes satiety and stabilizes blood sugar) to help support healthy hunger signaling.
READ: The 7 Best Natural Ways To Boost GLP-1 Levels
Avoid inflammatory foods like deep-fried or processed foods, especially processed meat, white flour, and refined carbs. Limit sugary foods and drinks, and alcohol.
Since inflammation is a primary factor in leptin resistance, eat more anti-inflammatory foods whenever you can. Common anti-inflammatory foods include:
- Berries
- Fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids
- Avocados
- Broccoli
- Green Tea
- Turmeric
- Dark chocolate
- Extra virgin olive oil
For more on how to eat to overcome leptin resistance, check out my article here.
Intermittent fasting is also a good strategy to combat inflammation, improve autoimmune conditions, and get your body weight to a happy place. It’s also good for the neurons in the brain responsible for energy expenditure and hunger signals.
Studies show periods of fasting reduce inflammation in the hypothalamus, your body’s link between your endocrine and central nervous systems (CNS). (10)
Reduce Your Stress Levels
Chronic stress is associated with high cortisol levels, which can increase inflammation and impair leptin signaling. Too much cortisol secretion can also promote body fat mass storage, especially in the belly.
Focus on managing stress through relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. Prioritize self-care, schedule breaks throughout the day, and engage in activities you enjoy that promote mental relaxation.
This may also mean prioritizing your work-life balance and learning the art of saying “no” to new responsibilities you can’t handle without excess stress. Reducing stress isn’t just good for leptin resistance. It’s essential to every aspect of your mental and physical health.
Shop This Article
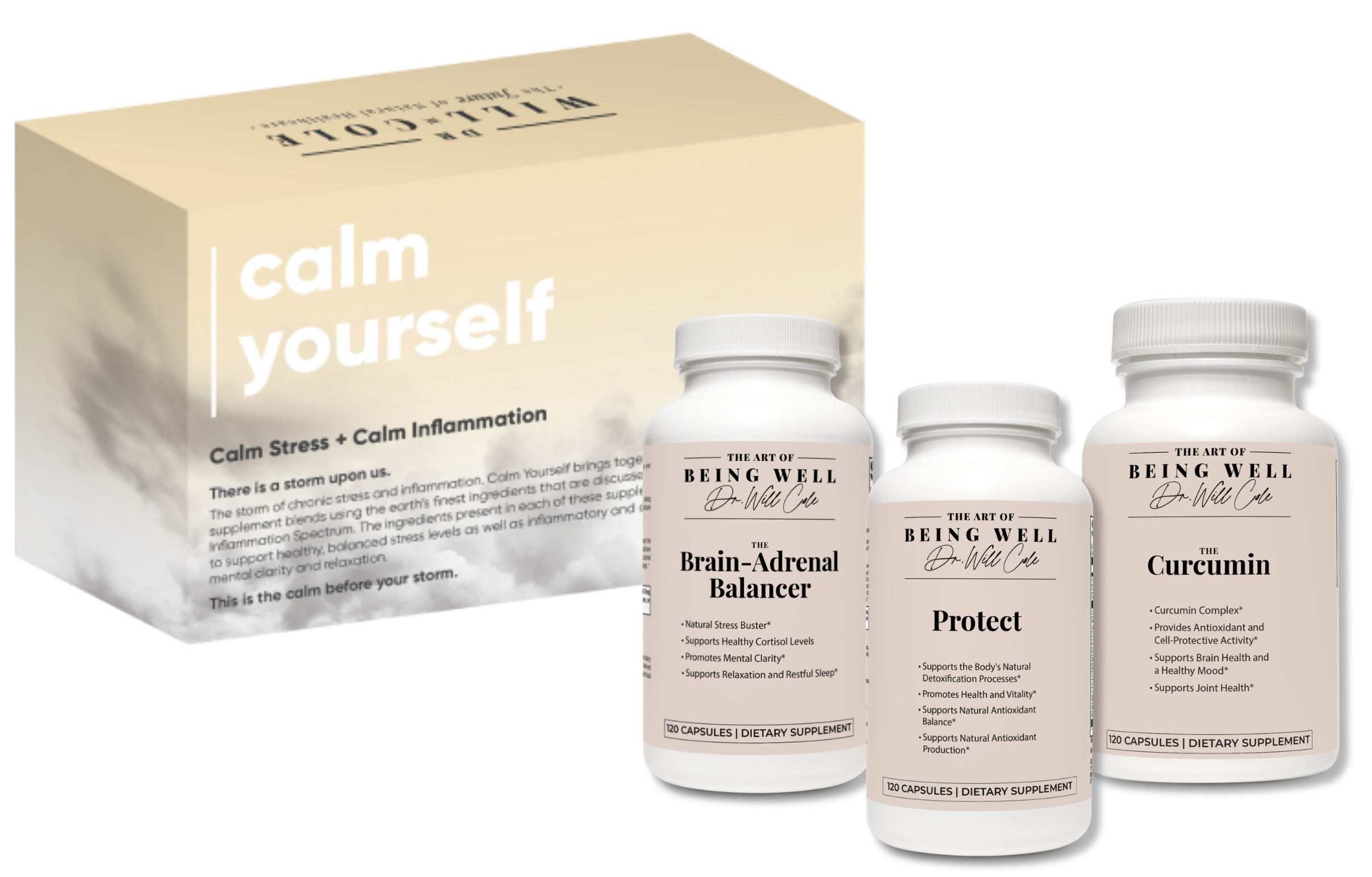
Struggling with stress management and balancing inflammation? Check out my Calm Yourself pack, a trio of supplements designed to combat inflammatory triggers and promote relaxation.
Try Detoxing
Detoxing can help reduce barriers to better hormonal balance. Processed foods, environmental pollutants, and synthetic chemicals can all contribute to your toxin load, trigger inflammation, and disrupt leptin signaling.
A detox can involve cutting out processed foods, sugar, and alcohol in favor of whole, antioxidant-rich foods. It can also involve identifying and removing environmental factors like mold toxicity. In addition to removing toxins from your environment, you'll want to work to clear accumulated toxins from your body.
Mold exposure is difficult to diagnose, but a functional provider would test for markers of chronic inflammatory response syndrome (CIRS). That may include elevated levels of the suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) gene and high cortisol levels.
You can learn all about how to detox in my guide here.
Prioritize A Form Of Exercise
Regular physical activity enhances your body’s sensitivity to leptin and helps reduce body fat, a key factor in leptin dysregulation. There is some evidence that high-intensity interval training (HIIT) is best for reducing inflammatory markers and your risk of chronic conditions. (11)
It’s most important to find a movement you enjoy and can stick with in the long term. That can look like a daily walking routine, swimming, or a combination of aerobic exercise and strength training. Getting out in nature is great for your emotional and physical well-being, too.
What About Leptin Supplements?
Leptin resistance plays a central role in obesity, making supplementation with leptin a logical potential treatment.
The problem is that most people with obesity and diet-induced obesity are already producing plenty of leptin. The issue isn’t a lack of circulating leptin, it’s a lack of response in the body to leptin. That’s why research consistently shows that leptin treatment is ineffective– elevated leptin levels don’t result in the metabolic responses we would want to see. Studies on both obese humans and diet-induced obese mice show that when introducing exogenous (produced outside of the body) or recombinant (lab-engineered) leptin, the body remains unresponsive and weight loss does not improve. (12)
Given this disconnect, researchers are looking into natural products that may be able to restore leptin sensitivity by targeting pathways involved in hormone signaling, including the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. (13)
At this stage, products marketed as leptin supplements don’t contain any leptin and typically are not connected to leptin action. These supplements, which are marketed as a way to help with appetite inhibition, weight loss, and leptin resistance, often contain ingredients like fiber or caffeine to curb your appetite and boost energy.
There are no medications to cure leptin resistance or serve as a leptin replacement, either. Some doctors may prescribe drugs that address the resulting symptoms, particularly in obese individuals.
That’s not getting to the root of your symptoms. It’s masking them. You may be dealing with adrenal fatigue, thyroid issues, or an undiagnosed gut condition getting in the way of optional health.
There may still be certain kinds of supplements that can help improve leptin resistance, combined with the strategies mentioned above, but these should be selected based on your unique case.
The best treatment option is one that examines your unique needs with a healthcare provider, specialist in endocrinology, or functional doctor to develop a quality plan.
How Functional Medicine Can Help
There isn’t just one way to approach leptin resistance. The most effective way to reverse a hormonal imbalance is to identify root causes and go from there.
The body is a big machine made of many codependent parts. My team and I offer an in-depth exploration of symptoms and labs accompanied by treatment plans tailored to your unique needs.
That’s at the heart of functional medicine. If you’re interested in a holistic approach to your hormonal health, schedule a consultation to optimize your wellness.
READ NEXT: How Functional Medicine Can Support Weight Loss
Image: Unsplash.com
View More At Our Store
Purchase personally curated supplements
and Dr. Will Cole’s books!

- Münzberg, H. & Heymsfield, S.B. (2019). New insights into the regulation of leptin gene expression. Cell Metabolism, 29(5), 1013-1014.
- Zhou, Y. & Rui, L. (2013). Leptin signaling and leptin resistance. Frontiers in Medicine, 7(2), 207-222.
- Pérez-Pérez, A., Sánchez-Jiménez, F., Vilariño-García, T., et al. (2020). Role of leptin in inflammation and vice versa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(16), 5887.
- Vilariño-García, T., Polonio-González, M.L., Pérez-Pérez, A., et al. (2024). Role of leptin in obesity, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(4), 2338.
- Simonds, S.E., Pryor, J.T., Ravussin, E., et al. (2014). Leptin mediates the increase in blood pressure associated with obesity. Cell, 159(6), 1404-1416.
- Younger, J., Kapphahn, K., Brennan, K., et al. (2016). Association of leptin with body pain in women. Journal of Women's Health, 25(7), 752-760.
- Pereira, S., Cline, D.L., Glavas, M.M., et al. (2021). Tissue-specific effects of leptin on glucose and lipid metabolism. Endocrine Reviews, 42(1), 1-28.
- Hebebrand, J., Hildebrandt, T., Schlogl, H., et al. (2022). The role of hypoleptinemia in the psychological and behavioral adaptation to starvation: Implications for anorexia nervosa. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 141, 104807.
- van Egmond, L.T., Meth, E.M.S., Engström, J., et al. (2023). Effects of acute sleep loss on leptin, ghrelin, and adiponectin in adults with healthy weight and obesity: A laboratory study. Obesity, 31(3), 635-641.
- García-Luna, C., Prieto, I., Soberanes-Chávez, P., et al. (2023). Effects of intermittent fasting on hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis, palatable food intake, and body weight in stressed rats. Nutrients, 15(5), 1164.
- Atakan, M.M., Li, Y., Koşar, Ş.N., et al. (2021). Evidence-based effects of high-intensity interval training on exercise capacity and health: a review with historical perspective. The International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(13), 7201.
- Tan, B., Hedbacker, K., Kelly, L., Zhang, Z., Moura-Assis, A., Luo, J. D., ... & Friedman, J. M. (2025). A cellular and molecular basis of leptin resistance. Cell Metabolism, 37(3), 723-741.
- Liu, Y., & Gong, F. (2025). Natural Products From Plants Targeting Leptin Resistance for the Future Development of Anti‐Obesity Agents. Phytotherapy Research.
Leptin resistance symptoms may include weight loss resistance or trouble keeping weight off, constant hunger or cravings, overeating, fatigue, overweight or obesity, brain fog, and joint pain.
If you have or suspect leptin resistance, make sure to avoid inflammatory foods like sugar, processed foods, and refined carbohydrates, which may further disrupt your hormone signaling pathways.
If your body isn’t responding to leptin, you may have trouble burning fat and losing weight. To improve leptin resistance, implement an anti-inflammatory diet and lifestyle routine, and explore possible root causes of inflammation and hormonal dysfunction.
The information on this website has not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration or any other medical body. We do not aim to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any illness or disease. Information is shared for educational purposes only. You must consult your doctor before acting on any content on this website, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition.
Our content may include products that have been independently chosen and recommended by Dr. Will Cole and our editors. If you purchase something mentioned in this article, we may earn a small commission.

BY DR. WILL COLE
Dr. Will Cole, DNM, IFMCP, DC is a leading functional medicine expert who consults people around the globe, starting one of the first functional medicine telehealth centers in the world. Named one of the top 50 functional and integrative doctors in the nation, Dr. Will Cole provides a functional medicine approach for thyroid issues, autoimmune conditions, hormonal imbalances, digestive disorders, and brain problems. He is also the host of the popular The Art of Being Well podcast and the New York Times bestselling author of Intuitive Fasting, Ketotarian, Gut Feelings, and The Inflammation Spectrum.

Gut Feelings
Healing The Shame-Fueled Relationship
Between What You Eat And How You Feel