Scleroderma Symptoms, Root Causes, and How To Find Relief

What is scleroderma?
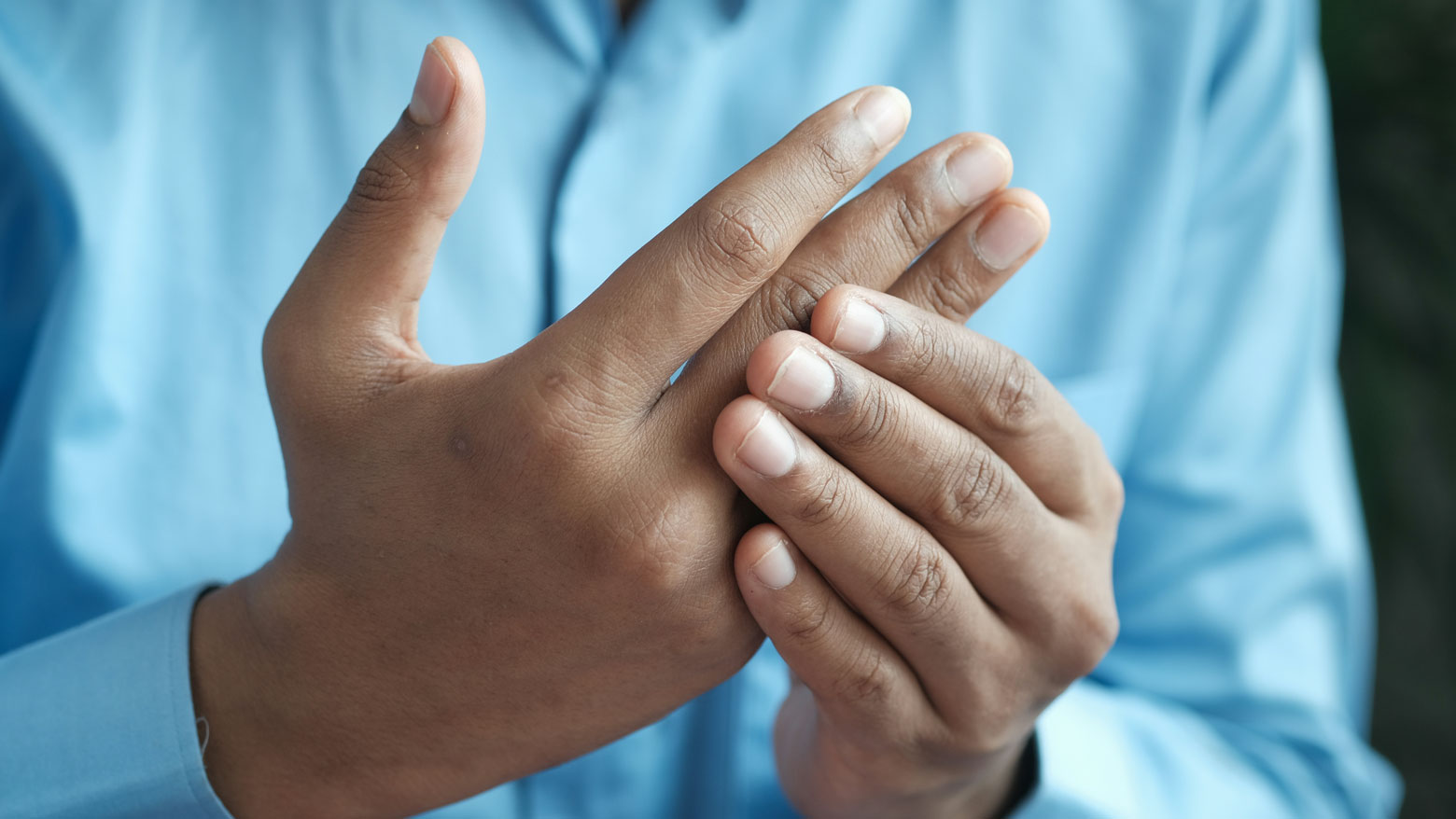
Scleroderma is a complex and often difficult-to-navigate condition that affects many aspects of the body. Essentially, your body’s immune system gets confused and decides to attack its own tissues, especially the skin and connective tissues. This autoimmune reaction leads to the hallmark symptom of scleroderma: thickening and hardening of the skin. This can be anywhere from mild, causing a few small patches of tough skin, to more severe, where it affects larger areas and even internal organs like the lungs, heart, or digestive system.
For someone living with scleroderma, the condition often spreads farther than just the skin. Internal complications can vary widely depending on which organs are involved. Some may experience difficulty breathing due to lung scarring (pulmonary fibrosis), while others might have digestive problems like acid reflux or difficulty absorbing nutrients. Joint pain and stiffness can also be common, making everyday movements a challenge.
Managing scleroderma requires a multidisciplinary approach. Doctors often use medications to help suppress the immune system's overactivity and reduce symptoms. Physical therapy can be beneficial for maintaining joint flexibility and mobility. Regular monitoring is crucial to catch any potential organ complications early on. Support groups and lifestyle adjustments, such as managing stress and maintaining a healthy diet, are helpful options to anyone managing this condition.
Scleroderma symptoms
- Early symptoms
-
-
- Fatigue
- Stiff, puffy fingers
- Fingers sensitive to cold
-
- Finger and joint symptoms
-
-
- Join pain or Stiffness - especially in the morning
- Color change in fingers
- Calcium bumps on fingers/bony areas
- Grating noise when moving inflamed tissue
- Immovable joints
- Pale, numb, or tingly fingers
- Sores on fingers
- Thick or swollen fingertips
-
- Digestive symptoms
-
-
- Heartburn
- Trouble swallowing
- Unexplained weight loss
- constipation/diarrhea
- Bloating
-
- Heart and lung symptoms
-
- Heart failure
- abnormal rhythms
- Shortness of breath
- Possible complications
- Kidney failure
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Cardiovascular disease
- Congestive heart failure
- Weak immune system
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- Cancer
If these symptoms look familiar to you, don’t hesitate to reach out to a trusted health professional to help you better understand and assess whether you may be suffering with scleroderma.
Types of Scleroderma
- Localized scleroderma - primarily affects the skin and sometimes the underlying tissues, without affecting major organs or organ systems
- Systemic sclerosis - a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the connective tissues of the body as well as internal organs (lungs, heart, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract)
- Diffuse sclerosis - characterized by widespread skin involvement that typically affects not only the hands, arms, and face but also extends to the trunk and sometimes the legs.
- Limited sclerosis (CREST syndrome) - is a subtime defined by 5 key features
- C - Calcinosis: Calcium deposits in the skin.
- R - Raynaud's phenomenon: Episodes of reduced blood flow to the fingers and toes in response to cold or stress.
- E - Esophageal dysmotility: Difficulty swallowing due to reduced muscle function in the esophagus.
- S - Sclerodactyly: Thickening and tightening of the skin on the fingers and toes.
- T - Telangiectasia: Small red spots on the skin caused by widened blood vessels.
What causes scleroderma
Let's break down scleroderma and its origins. Essentially, it's an autoimmune condition where the body's defense system gets “confused” and attacks its own tissues instead of dangerous cells or pathogens. This attack leads to an overproduction of collagen, the protein responsible for skin and tissue structure. This excess collagen causes the skin and sometimes internal organs to become stiff and harden—hence the name, which comes from Greek words meaning "hard skin."
Doctors aren't entirely sure what causes this autoimmune response in scleroderma. It's believed to possibly involve a mix of genetic predisposition and environmental factors, possibly including viral infections or exposure to certain chemicals. Researchers are still looking into the exact mechanisms, but one thing's for sure: the immune system's gone a bit haywire.
What triggers a scleroderma flare up?
Unfortunately, flare ups can be just as unpredictable as they are difficult to manage. Some common flare triggers include:
- Cold weather
- Viral or bacterial infections (like the common cold)
- Dietary flare ups
- Stress
- Medication changes
- Inflammatory lifestyle
What risk factors are associated with scleroderma?
- Assigned female at birth (AFAB)
- Ages 30-50
- Black Heritage
How is scleroderma diagnosed
In traditional medical settings, diagnosing scleroderma typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history review, and specialized tests. Diagnostic tests play a crucial role, with blood tests often used to detect specific antibodies associated with scleroderma, such as anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA), anti-centromere antibodies (ACA), or anti-Scl-70 antibodies. Imaging studies like high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scans may be performed to assess lung involvement, while echocardiograms can evaluate heart function. Skin biopsies may also be taken to examine tissue under a microscope for confirmation.
In alternative or functional settings, approaches to diagnosing scleroderma may vary widely depending on the practitioner's background and the specific modalities used. Some alternative or complementary healthcare providers may rely on symptom patterns, physical examinations, and patient-reported experiences to assess and diagnose scleroderma.
How scleroderma is treated
In a traditional medical setting, doctors have a host of tools at their disposal. Unfortunately, many of these interventions can have serious side effects including the use of immunosuppressants, anti-inflammatory drugs, and even stem cell transplants.
While the condition is complex and individual benefits from a variety of intervention types, the functional approach recommends treating the root of inflammation to the highest degree possible, so that interventions with negative side effects can be used more sparingly.
Begin Healing From Scleroderma Naturally
Exercise: Getting regular physical activity not only boosts circulation but also keeps your joints flexible and reduces stiffness. Plus, it’s great for basically every system working to keep your body and mind healthy.
Protect your skin: Shielding your skin from injuries and excessive sun exposure can really help keep those flare-ups at bay and protect against long-term skin damage.
Stop smoking: Kicking the habit is crucial because smoking can make scleroderma symptoms worse and increase the risk of complications. It's a big win for your overall health and managing the disease.
Managing heartburn: Acid reflux and heartburn are common issues with scleroderma. Making changes to your diet can make a big difference in how you feel day to day.
Bundle up: When it's chilly out, bundling up and avoiding prolonged cold exposure can go a long way in preventing flare-ups and minimizing any discomfort.
Functional medicine tackles scleroderma treatment and other health challenges from a holistic perspective, aiming to uncover and tackle the root causes of disease rather than just treating symptoms. The key is crafting a personalized treatment roadmap that fits each person's specific needs and circumstances.
This approach dives deep into aspects like diet, lifestyle choices, gut health, and environmental influences to better manage scleroderma symptoms and enhance overall well-being. Ready to take charge of your health? Consider scheduling a consultation to explore how functional medicine can support your journey toward better health and symptom management.
Start Your Health Journey Today
FUNCTIONAL MEDICINE CONSULTATIONS FOR PEOPLE AROUND THE WORLD
The information on this website has not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration or any other medical body. We do not aim to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any illness or disease. Information is shared for educational purposes only. You must consult your doctor before acting on any content on this website, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition.
Our content may include products that have been independently chosen and recommended by Dr. Will Cole and our editors. If you purchase something mentioned in this article, we may earn a small commission.

BY DR. WILL COLE
Dr. Will Cole, DNM, IFMCP, DC is a leading functional medicine expert who consults people around the globe, starting one of the first functional medicine telehealth centers in the world. Named one of the top 50 functional and integrative doctors in the nation, Dr. Will Cole provides a functional medicine approach for thyroid issues, autoimmune conditions, hormonal imbalances, digestive disorders, and brain problems. He is also the host of the popular The Art of Being Well podcast and the New York Times bestselling author of Intuitive Fasting, Ketotarian, Gut Feelings, and The Inflammation Spectrum.

Gut Feelings
Healing The Shame-Fueled Relationship
Between What You Eat And How You Feel